 The limbic system, often referred to as the “emotional brain,” plays a fundamental role in shaping our emotional experiences, regulating our responses to stress, and influencing our psychological health.
The limbic system, often referred to as the “emotional brain,” plays a fundamental role in shaping our emotional experiences, regulating our responses to stress, and influencing our psychological health.
Comprising interconnected structures deep within the brain, the limbic system orchestrates complex processes involved in memory formation, emotional processing, and behavior modulation.
Understanding the intricate workings of the limbic system provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying emotional and psychological well-being.
Today, we delve into the fascinating realm of the limbic system, exploring its anatomy, functions, and profound impact on our emotional and psychological health.
Anatomy of the Limbic System
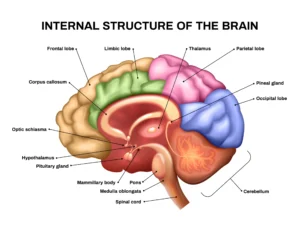
The limbic system is a network of structures located within the brain’s temporal lobe, including
- Amygdala. Often regarded as the “emotional hub” of the brain, plays a central role in processing emotions such as fear, anger, and pleasure.
- Hippocampus. Is crucial for memory formation and consolidation.
- Hypothalamus. Regulates basic physiological functions such as hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior.
- Cingulate gyrus.
These structures are interconnected through intricate neural pathways, facilitating communication and coordination of emotional and cognitive processes.
Emotional Processing
One of the primary functions of the limbic system is the processing and regulation of emotions. The amygdala evaluates incoming sensory information and determines its emotional significance, triggering appropriate behavioral and physiological responses. For example, when faced with a perceived threat, such as encountering a predator, the amygdala initiates the “fight or flight” response, activating the sympathetic nervous system to prepare the body for action.
Conversely, the limbic system also plays a role in experiencing positive emotions such as joy, love, and contentment, enhancing our capacity for social connection and interpersonal relationships.
Memory Formation and Consolidation
The hippocampus, a key component of the limbic system, is essential for memory formation and consolidation. It processes incoming information from sensory inputs and encodes it into long-term memory, allowing us to recall past experiences and events. Damage to the hippocampus can impair memory function, leading to difficulties in learning and remembering new information.
Additionally, the limbic system interacts with other brain regions involved in memory, such as the prefrontal cortex and the basal ganglia, to integrate emotional and cognitive aspects of memory processing.
Stress Response and Regulation
The limbic system plays a crucial role in modulating our responses to stress and adversity. The hypothalamus, in conjunction with the pituitary gland and the adrenal glands, coordinates the body’s stress response by releasing stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Chronic stress can dysregulate the limbic system, leading to heightened anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Conversely, practices such as:
- mindfulness meditation,
- deep breathing exercises, and
- relaxation techniques can help regulate the limbic system’s stress response and promote emotional resilience.
Implications for Mental Health
Dysfunction in the limbic system is implicated in various mental health disorders, including
- anxiety disorders,
- depression,
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and
- bipolar disorder.
Imbalances in neurotransmitter systems and alterations in limbic circuitry contribute to symptoms such as:
- mood disturbances,
- emotional dysregulation, and
- impaired memory function.
Understanding the role of the limbic system in these disorders is critical. It’s essential for developing targeted interventions and treatments to alleviate symptoms and improve overall psychological well-being.
The limbic system serves as a cornerstone of our emotional and psychological health, orchestrating a symphony of neural processes that underpin our experiences of emotion, memory, and behavior. By unraveling the complexities of the limbic system’s anatomy and functions, researchers and clinicians gain valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying emotional and psychological disorders.
By nurturing the health and resilience of the limbic system through lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, and therapeutic interventions, individuals can cultivate greater emotional awareness, resilience, and well-being in their lives.
Picture Credit: Freepik
